Right Angle – Definition, Example and Properties
Right Angle – Definition, Example and Properties
What is a right angle?
When two straight lines are perpendicular to each other or intersect at 90º, they form a right angle.
A right angle is represented by the symbol L.
In our daily life we can see many real-life examples of the right angles. We can see right angles in the edges of a door, corner of a room, cube, book, windows, chair, screen of a mobile and at several other places.
Intersection of a vertical and a horizontal line mostly make a right angle. The diagonals of a rhombus, kite, square, intersect at 90, therefore, the angle of their intersection is a right angle.
Right angle Definition:
If the measure of the angle between two rays is exactly equal to 90º then the angle is called a right angle. In radians, it is represented as 𝜋/2.
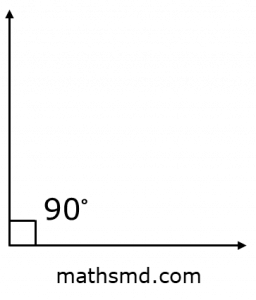
A right angle is an angle that is that is equal to 90 degrees. Angles whose measures less than 90º such as 23º, 75º , 88º , 67º etc. are acute angles and angles which measures more than 90º such as 95º , 100º , 123º , 154º , etc. are called obtuse angles.
How to draw a right angle using a protractor?
Step 1: Draw a straight line.

Step 2: Place the protractor on the horizontal line.
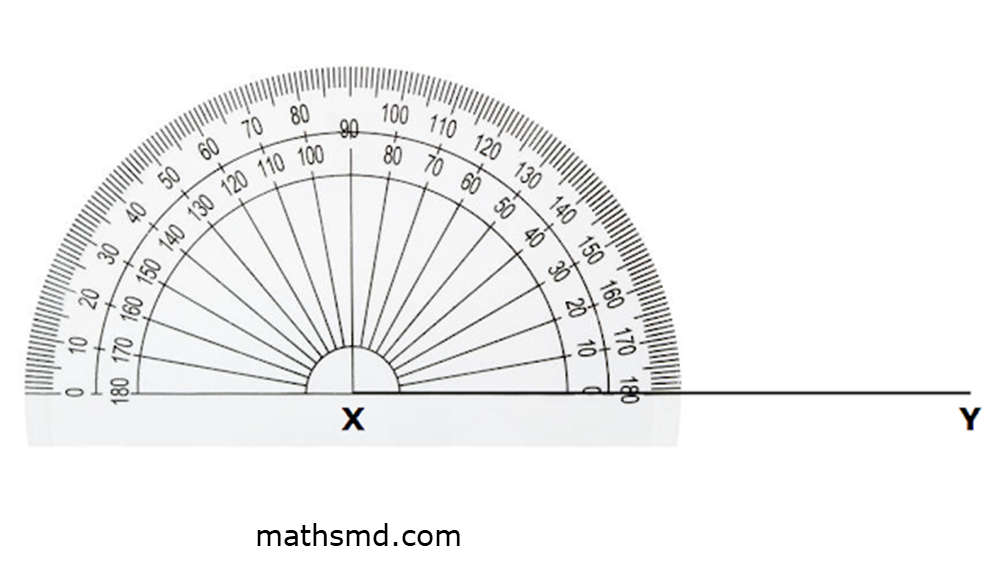
Step 3: Measure the angle 90º and mark it with a point. Using a scale, draw a straight line from this point to the horizontal line.
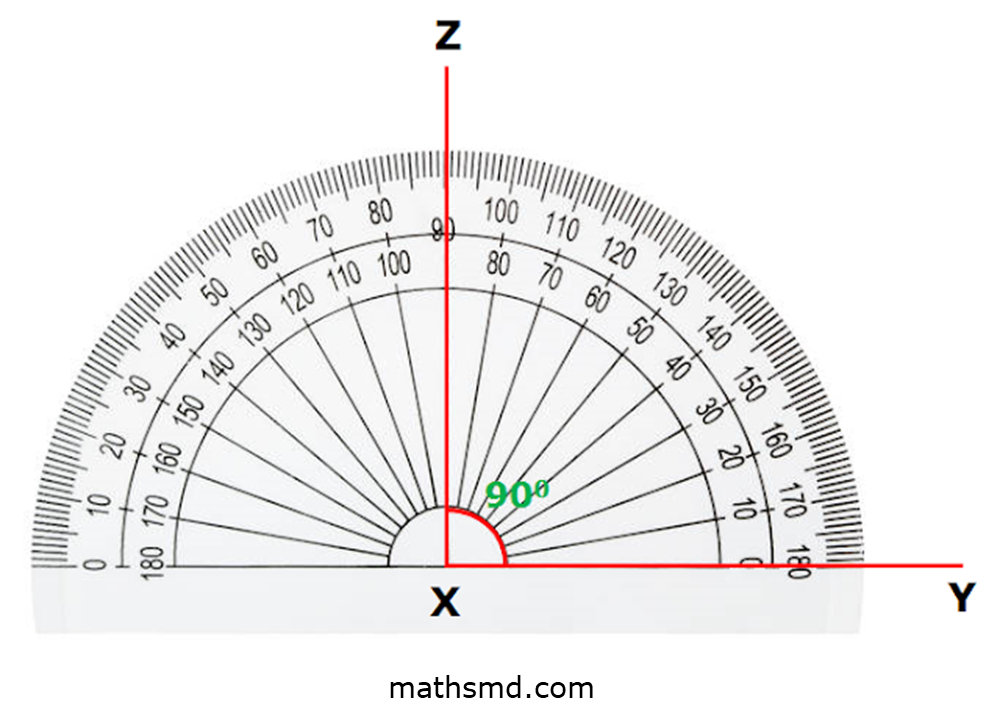
Step 4: ∠ZXY is a right angle.
