Parts of a Circle – Definition, Examples and Formula – Radius – Diameter – Chord – Circumference – Arc – Area – Sector –
We use many objects in our daily life, which are round in shape, such as wheels of a vehicle, sun, moon, a dinner plate, button of shirts etc.
These are real examples of a circle.
Let’s study about circle and it’s parts.
Definition:
1. Circle
A circle is a collection of all the points in a plane, whose all points are same distance from a fix point.
A circle named by its center. Thus, this circle is called circle A. It’s center is at point A.
The fixed point is called the center of the circle, and the distance between center and any point on the circle is called the radius of the circle.
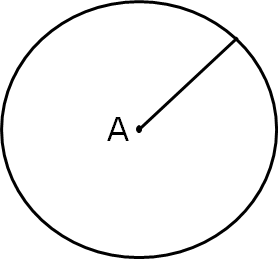
2. Center
The point equidistant from the points on the circle is known as “Center”.
Here is a circle with center A.
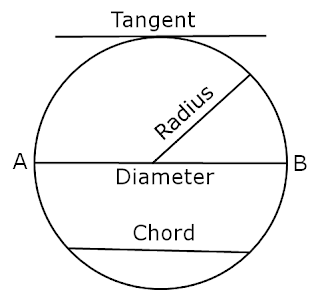
The longest distance that has the end points on the circle and passes through the center is called “Diameter”.
It is a special chord(longest chord) and it is twice of radius.
Diameter denoted by D.
Diameter = 2 x radius
Radius = Diameter/2
4. Radius
The distance from center of a circle to any point on the circle, is “Radius”, It is half of diameter.
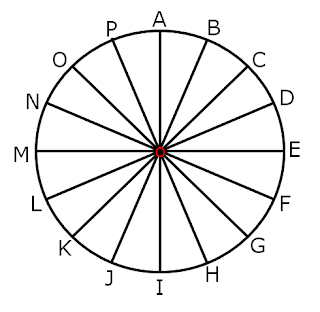
Infinite radii can be drawn for any circle. OA, OB,
OA, OB, OC, OD, OE, OF, OG, OH, OI, OJ, OK, OL, OM, ON, OO, OP, are the radii of circle O.
5. Chord
A line segment joining two end points, that lie on a circle is “Chord”. Infinite radii can be drawn for any circle.
6. Circumference
The length of the complete circle is called its “Circumference”.
The formula of circumference is C = 2𝜋r
Where C is the circumference and r is the radius of the circle.
circumference is also given by
C = 2
2 x radius = diameter
∴ C = 𝜋d
The value of 𝜋 is 22/7 or 3.14159
7. Exterior and Interior of a Circle
In a plane which the circle lies divided it into three parts.
a. Inside the circle, which is called the “Interior of the circle”.
b. Circle itself.
c. Outside the circle, which is called the “Exterior of the circle”.
8. Arc
An arc is a portion of the circumference of a circle. It is also known as circular arc.
simply, A piece of a circle between two points is called an “Arc”.
9. Major arc and Minor arc
There are two pieces, one is longer and other is smaller. The longer piece is called the “Major arc” and the smaller piece is called the “Minor arc”.
The major arc is denoted by ⌒
PRQ
⌒
and minor arc is PQ .
When P and Q are ends of a diameter, then both arcs are equal and each is called a Semicircle.

10. Central angle of a circle
Central angle is an angle whose one vertex lies on the center of the circle and two radii meet at the center of the circle. ∠AOB is the central angle in figure.
11. Semi circle
A semi circle is half of the circle.
Circumference of a semi circle = Half of the perimeter of a circle + length of the diameter
= (2𝜋r/2) + 2r
= 𝜋r + 2r
= r(𝜋 + 2)
Circumference of a semi circle = r(𝜋 + 2)
12. Area of a circle
Area of a circle is A = 𝝿r2
= 𝝿 (pi)x (radius)2 , where r is radius of the circle.
or when we know the diameter A = (𝝿/4) x D2
When we know circumference A = c2/4𝝿
13. Sector
A sector is the area covered by two radii and a minor arc and or major arc.
ACB and AOB are two of the sectors in circle.
The total angle of a circle is 3600 .
Area of sector = (𝜃/360) x 𝝿r2
Length of minor arc = (𝜃/360) x 2𝝿r
Length of major arc = (360 – 𝜃/360) x 2𝝿r
14. Tangent of a circle
A straight line that intersects the circle, at only one point is a “Tangent”.