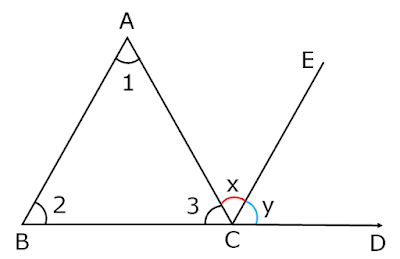
Exterior Angle of a Triangle – Theorem
Exterior Angle of a Triangle
If any side of a triangle is extended then the exterior angle of triangle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles.
Given : A △ABC, side BC of △ABC is extended,
∠ACD is an exterior angle.
To Prove : The sum of measure of exterior angle of triangle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles. so,
m∠ACD = m∠BAC + m∠ABC
Construction: Draw a line CE parallel to side BA through C.
Proof : BA ∥ CE and AC is a transversal.
Therefore, ∠1 = ∠x ….(i) (pair of alternate angles)
BA ∥ CE and BD is a transversal.
Therefore, ∠2 = ∠y ….(ii) (pair of corresponding angles)
add eq. (i) and (ii) we get
∠1 + ∠2 = ∠x + ∠y
Now, ∠x + ∠y = ∠ACD (From figure)
Hence, ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠ACD
∠BAC + ∠ABC = ∠ACD
∠ACD = ∠ABC + ∠BAC
We see that the exterior angle of triangle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles.
Hence Proved.