Addition Property Of Equality – Definition – Examples
Equality – Addition Property
Definition:
Addition property of equality states that if using the same mathematical operation(same number is added) on both sides of an equation, then both sides of equation will remain equal.
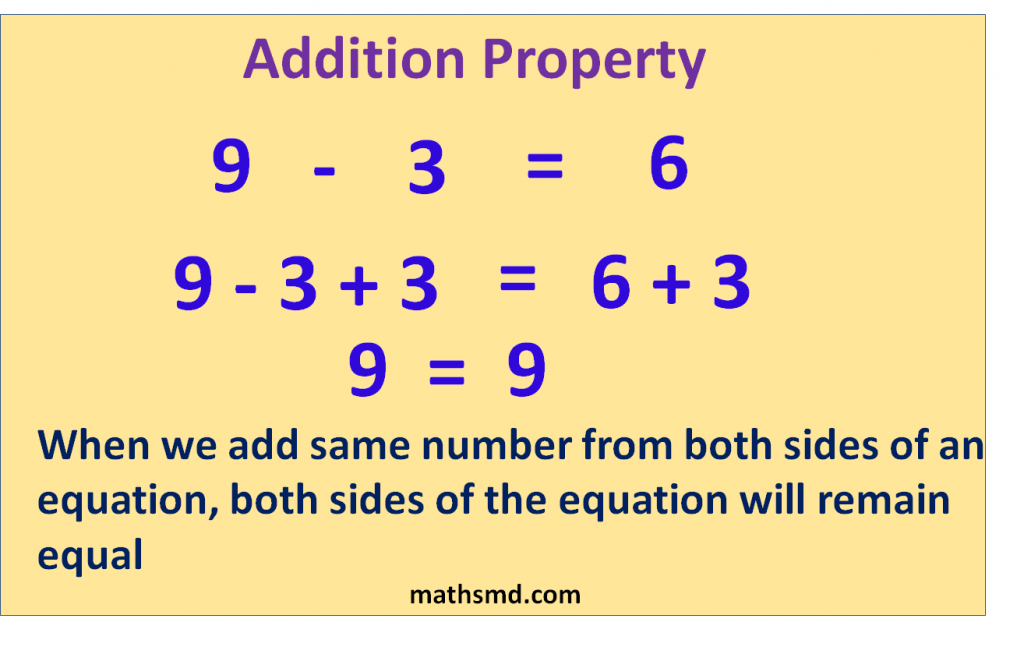
In above example, we add 3 on both sides. When we add 3 left side we get (9 – 3 + 3 = 9), and when we add 3 on right side we get (6 + 3 = 9). It means in a equation, without changing the solution of the equation same number may be added from both sides.
This property used to solve equivalent equations.
Example: x – 5 = 8
Here, x is unknown and we want to find the value of x. So if we add 5 from one side of the equation, we also add 5 from the other side of the equation to keep the equation the same.
x – 5 + 5 = 8 + 5
x = 13
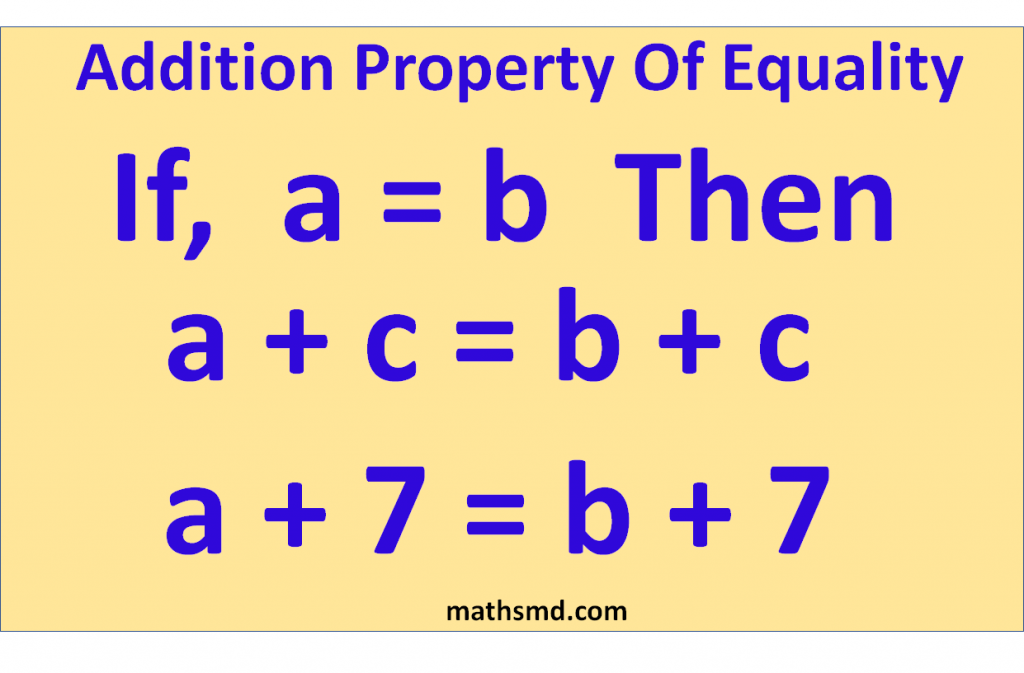
Formula
The formula of addition property of equality is
If a = b
then, a + c = b + c
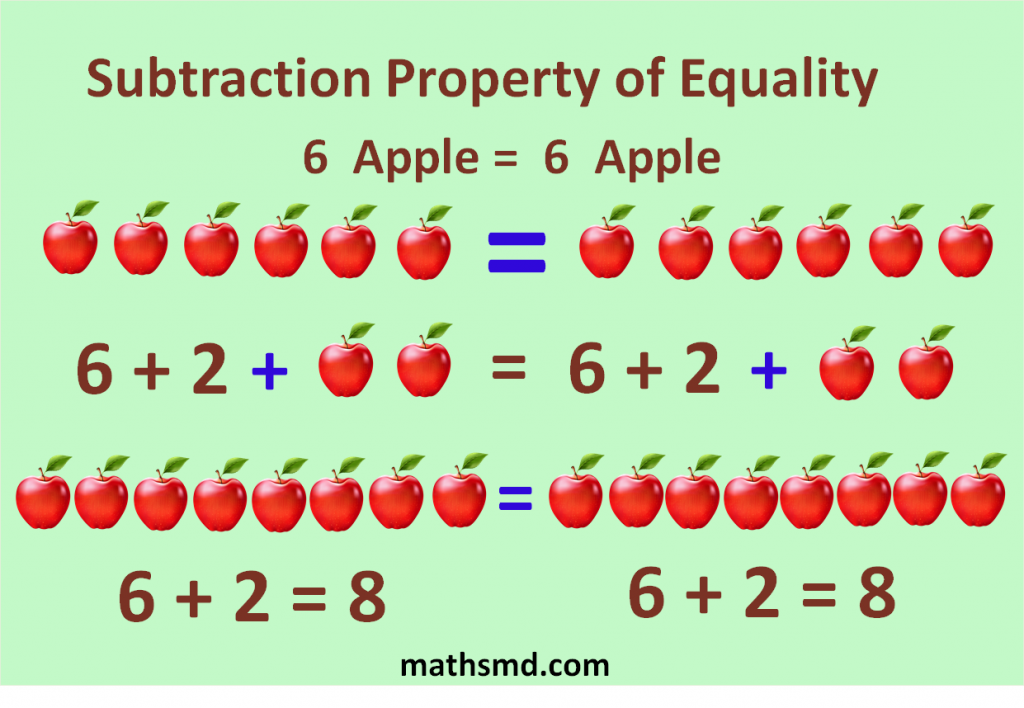
For example: If we have 2 sets of apples and both sets have 6 apples, we want to add 2 apples from 1 set.
So we would also have to add 2 apples from the other set of apples to keep them the same.
We get 8 apples both sides.
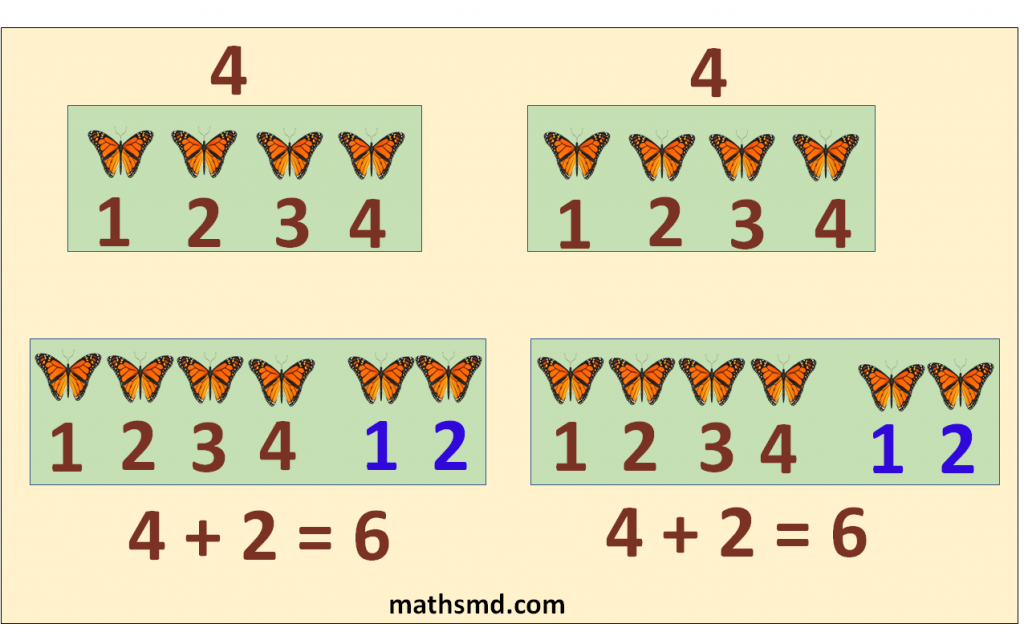
We have to do same to both sides of the equation.
Example: Here, A and B are two sets of butterflies. Set A have 4 butterflies and set B also have 4 butterflies.
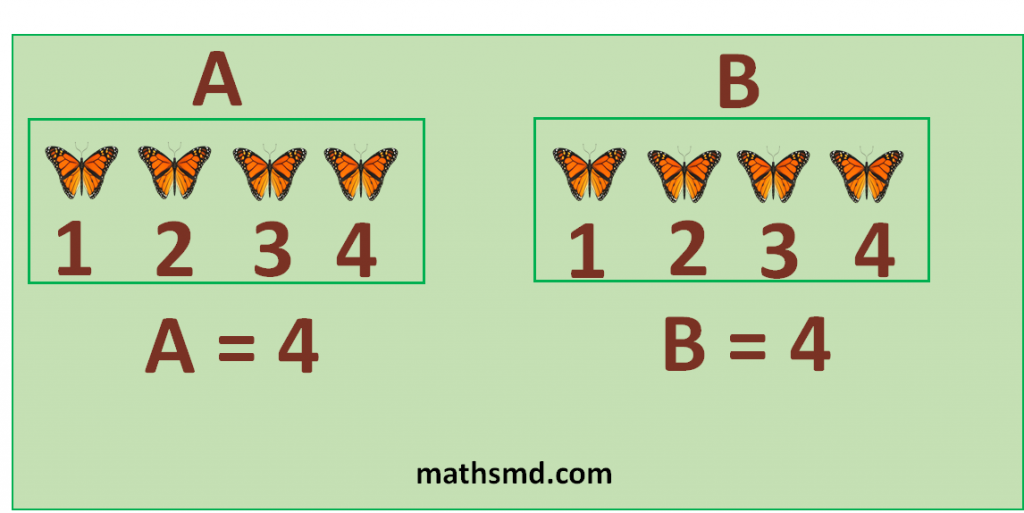
Now we add 2 butterflies from both sets. We get 6 butterflies in both sets. So our equation is balanced, both sides have 6 butterflies.