Integer – Definition – Example
Integer – Definition – Examples
The term “Integer” originated from Latin. “Integer” means whole.
Integers are set of whole numbers and negative numbers.
Here, we are discuss about integers in brief.
Definition:

Example: 3, 4, -6, -357, -4657, 98523, all are integers.
The set of integers is denoted by symbol “Z”.
Z = {…..-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,…..}
Note: Integers are (Counting numbers + Zero + Negative numbers).
Type of Integers
Integers are comes in three types
(i) Zero (0)
(ii) Positive Integers
(iii) Negative Integers
Zero is neither a positive integer nor a negative integer.
Positive Integers: An integer is positive, if it is greater than zero.
Positive integers are called counting numbers or natural numbers.
These integers are sometimes denoted by (Z+).
Example: Z+ = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,…..)
Negative Integers: An integer is negative, if it is less than zero.
The negative integers are negative of natural numbers.
These integers are sometimes denoted by (Z-).
Z- = (-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9, -10, -11, -12, -13, -14, -15, -16, -17, -18, -19, -20, -21, -22, -23, -24, -25,…..)
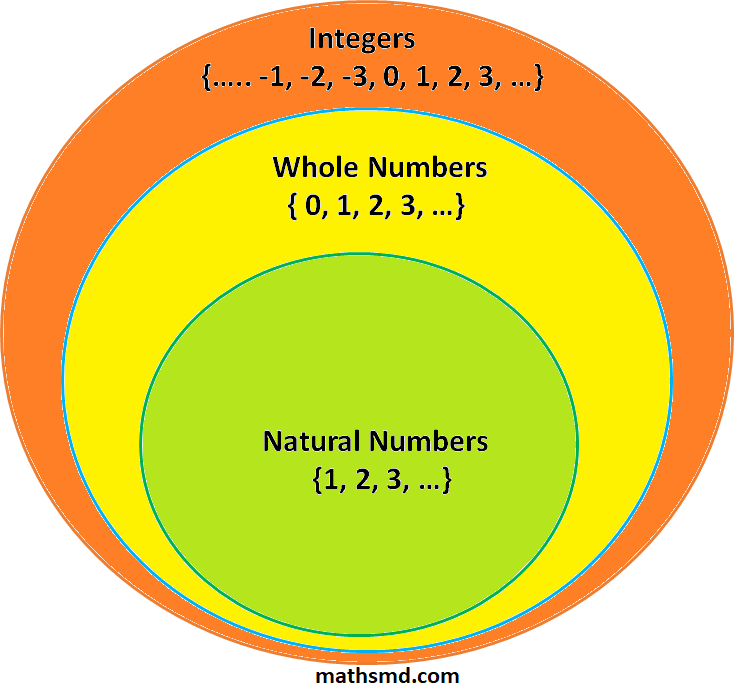
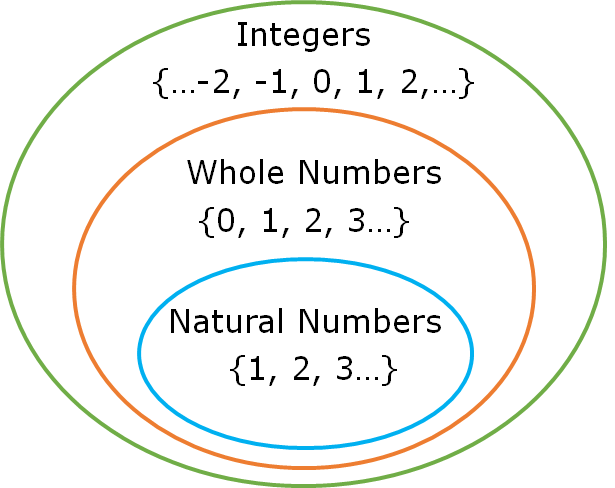
1/2, 99/5, 3/5, 2.3, 7.91 all are not integers because these are either fraction or have decimal part.
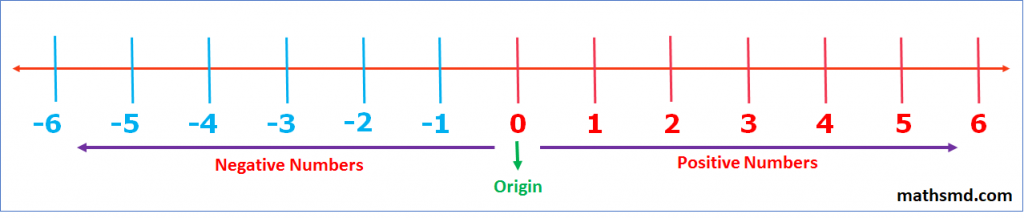
This is a number line for Integers.
Positive integers are lie on the right side of the 0 on number line.
Negative integers are lie on the left side of the 0 on number line.