Angle Bisector – Definition – Examples – Geometry
Angle Bisector – Definition -Examples
The angle(interior) bisector of an angle is a line or line segment that divides the angle into two (congruent)equal parts.
The angle bisector is also called the internal angle
bisector.
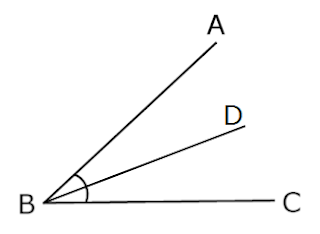
In ∠ABC, BD is angle bisector of ∠ABC.
In above figure BD is bisect the ∠ABC.
∵ ∠ABC = 900
∴ ∠ABD = 450
and ∠DBC = 450
∠ABD and ∠DBC are congruent
Note- Any point on angle bisector is equidistant from the to sides of the angle.
In below figure BD is angle bisector of ∠ABC. Find the measure of ∠ABC.
BD is an angle bisector, of ∠ABC,
∴ ∠CBD = ∠ABD
∵ ∠CBD = 350
∴ ∠ABD = 350
Therefore, ∠CBD = 350, BD is angle bisector
∵ ∠ABC = ∠ABD + ∠CBD
Substituted the value of ∠ABD and ∠CBD
∴ ∠ABC = 350 + 350
∴ ∠ABC = 700