The Pythagoras Theorem
The Pythagoras Theorem
A long time over 2000 years ago, a Greek mathematician named Pythagoras discovered an amazing and interesting property about Right triangles,
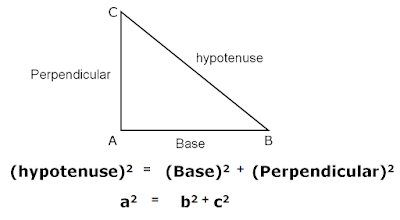
The square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
This property now called Pythagoras or Pythagorean Theorem.
In mathematics, the longest side of a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle is known as hypotenuse.
Pythagoras theorem applies to right triangles and states that,
The square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
or
The square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
(hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2+(Perpendicular)2
a2 = b2 + c2
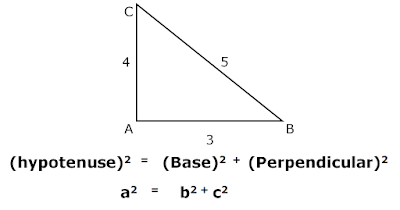
Example: In below right triangle length of base is 3, and length of perpendicular is 4. Find the length of hypotenuse.
Solution:
We know from pythagoras theorem,
(hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2+(Perpendicular)2
a2 = 32 + 42
a2 = 9 + 16
a2 = 25
a = 5
Therefore, hypotenuse is 5.