Angle – Definition – Parts Of Angles
Angle – Definition – Geometry
Definition:
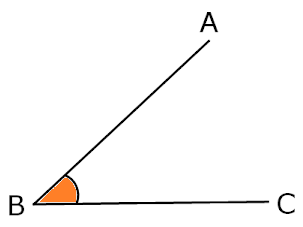
In plane geometry, angles are formed by two rays or lines called the arms or sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.


Angle Symbol
An angle is represented by symbol ∠
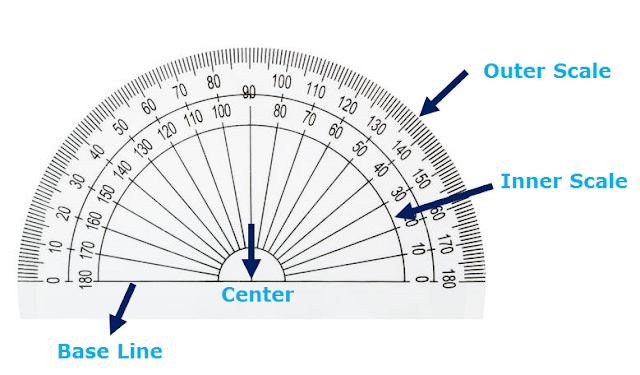
Angles are measured in degree, which is unit of angle using a protractor.
Angles Name

Here angle name is ∠ABC.
Angles name are usually using alphabet letters to identify the different parts of the angle the vertex and rays.
For example, in below figure ∠AOB, identifies an angle with “O” as the vertex.

It is enclosed by the rays A and B. Sometimes it is simply called angle “O.”
In below figure angle ∠ABC, identifies an angle with “B” as the vertex.
Parts of angle
1. Arms or Sides
2. Vertex
3. Initial Side
4. Terminal Side
1. Arms or Sides: The two rays that formed the angle are called the arms or sides of the angle.
Here OA and OB are arms or sides of the ∠AOB

2. Vertex: The common end point where two rays meet together to form an angle is called the vertex of the angle.
Here O is the vertex of the ∠AOB

3. Initial Side: Initial side is also known as the reference line. As a reference line all measurements of angles are done taking this line.
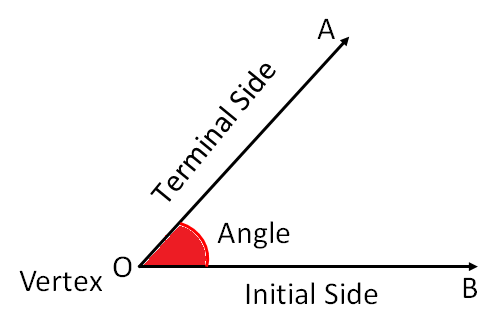
4. Terminal Side: Terminal side is the side where the measurements of the angle up to done.
Positive Angle and Negative Angle
Positive Angle: An angle measured in Anti-clockwise (Counterclockwise) direction is a positive angle.

Negative Angle: An angle measured in clockwise direction from the base is a negative angle.

Congruent angles
Two angles with the same measure are called congruent angles.
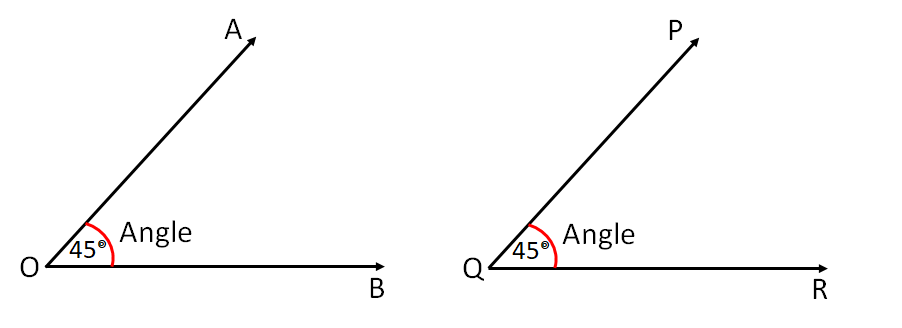
Congruent angles are denote as ∠O ≅ ∠Q
Here two angles ∠AOB and ∠PQR same in measure, both are 45º.
History of word angle
The word “angle” comes from the Latin word angulus means corner. It is also related to the Greek word ankylos means “crooked, curved.” The English and Greek words come from the proto-Indo-European root word “ank” meaning “to bend” or “bow.”
